
Pes planus in adult patients is not significantly associated with hallux valgus severity and recurrence, radiographic outcomes, or clinical scores.Ĭopyright © 2020 the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. A rigid flatfoot deformity caused by a malpositioned navicular bone at the neck of the talus the ankle is in severe equinus and the forefoot in dorsiflexioni.e., rocker bottom-likeaccompanied by contraction of the talonavicular. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary Farlex 2012. Synonym(s): pes abductus, pes pronatus, pes valgus. Multivariable logistic regression revealed that none of the radiographic parameters for pes planus affected hallux valgus recurrence. permanent eversion of the foot, the inner side alone of the sole resting on the ground it is usually combined with a breaking down of the plantar arch. A significant interaction between the time points and groups was not observed with respect to the hallux valgus angle (p =. 001, respectively) however, a significant difference was not noted between the pes planus and non-pes planus groups (p =. The hallux valgus angle and inter-metatarsal angle changed significantly after the surgery (p <.
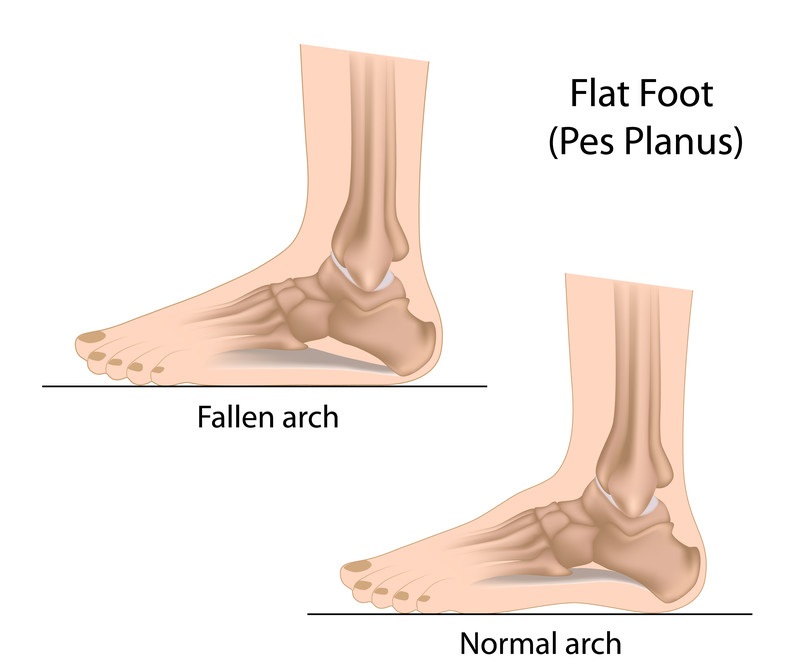
A significant correlation between radiographic parameters of pes planus and hallux valgus severity, radiographic outcomes, Foot and Ankle Outcome Score, and Foot Function Index were not noted. The Foot and Ankle Outcome Score and Foot Function Index were evaluated. The hallux valgus angle, inter-metatarsal angle, lateral talo-first metatarsal angle, calcaneal pitch, and talonavicular coverage angle were measured.
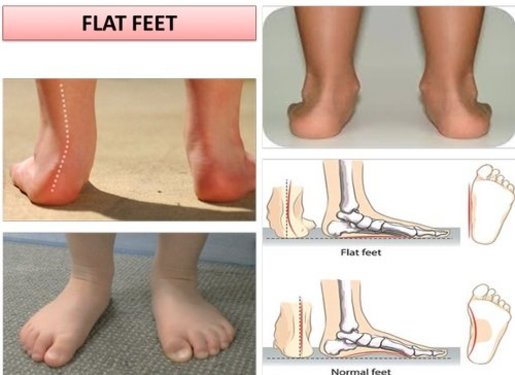
A total of 122 feet were retrospectively analyzed after hallux valgus surgery.

This study aimed to determine whether the degree of pes planus was associated with hallux valgus severity and hallux valgus surgery outcomes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
